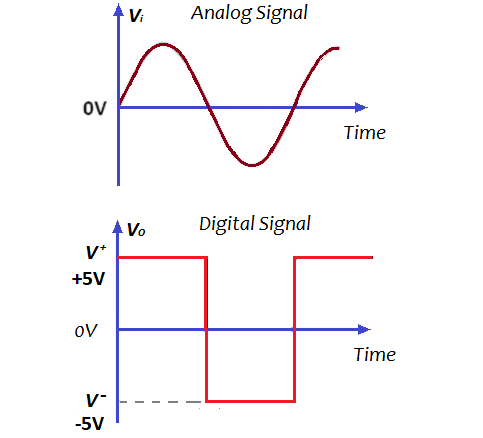
The basic difference between analog and digital signals is that an analog signal is a continuous signal whereas a digital signal is a discrete signal.
Analog and digital signals
When an electronic device shows us information, it can do it analogically or digitally. Analog means that the information, the signal, to pass from one value to another passes through all the intermediate values, it is continuous. On the other hand, digital signals jump from one value to another without taking intermediate values into account.
An analog signal is continuous and can take infinite values. A digital signal is discontinuous, and can only take two values or states: 0 and 1, which can be low and high voltage electrical impulses, open or closed switches, etc.
What are analog and digital signals?
Analog Signals
It is a type of time-varying continuous signal that is divided into composite and simple signals.
Analog signals are generally sine waves, which cannot be decomposed. On the other hand, a composite type of analog signal can be decomposed into many sine waves.
An analog signal can be defined using amplitude, time period if not frequency, and phase. Amplitude streaks the highest pitch of the signal, Frequency streaks the rate at which an analog signal varies, and Phase streaks the position of the signal relative to time nothing.
An analog signal is not noise resistant, so it faces distortion and reduces the transmission quality. It is not possible to fix the range of analog signal values.
Digital signal
Similar to analog signals, digital signals carry data although it is a bit different. These signals are discrete or non-continuous.
A digital signal carries data in the form of binary as it means in bits. Also, these signals can be broken down into sine waves called harmonics.
Like analog signals, digital signals have amplitude and frequency, and phase. We can define the digital signal by bit interval as well as by bit rate. Here, bit interval is nothing but the time required to transmit a single bit, while bit rate is the frequency of bit interval.
Digital signals are more resistant to noise, therefore, they hardly face any distortion. These waves are simple to transmit and more reliable, unlike analog waves. Digital signals include a limited variety of values between 0 and 1.
Difference between Analog and Digital Signals
| Analog signals | Digital Signals |
| It is a continuous & time-varying signal. | It has only two states. It has binary states 0 & 1. |
| An analog signal is usually in the form of a sine wave. However, it may be also in the form of triangular, sawtooth, or any time-varying form. | A Digital signal is usually in the form of a square wave that represents two states of the signal. |
| It is difficult to troubleshoot the analog circuit. | It is easy to troubleshoot digital circuits. |
| They are sensitive to noise. The analog signal can catch the noise signal. | Digital signals are not prone to noise. |
| The noise can affect the accuracy of the analog signals. | The noise can not affect the accuracy of the analog signals. |
| Analog signals may pick the noise during signal transmission. | The Digital signal does not pick up the noise during signal transmission. |
| Analog signals use more power. | Digital signals are less powerful. |
| Examples of the analog signal are temperature, pressure, flow measurements, etc. | Examples of digital signals are valve feedback, Motor Start, Trip, etc. |
| Major components of the analog circuits are resistors, Capacitors, Inductors, Diodes | Major components of the digital circuits are ICs, Microcontrollers, etc. |
The original article website:
https://www.electricalvolt.com/2022/04/what-are-analog-and-digital-signals-differences-examples/?fbclid=IwAR21H_kpuQvaI4FCK3yTsy5OPPX8qBx6CgthlveSiqAgDp_llmkLBvESq7M